Colorectal cancer is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States. Colorectal cancer screening is recommended for all adults aged 50 and older. Early detection and treatment of colorectal cancer can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Editor's Note: Colorectal Cancer: Advanced Detection And Treatment Strategies For Improved Patient Outcomes have published today date.
In recent years, there have been significant advances in the detection and treatment of colorectal cancer. These advances have led to improved patient outcomes, including increased survival rates and reduced recurrence rates.
Key differences of some treatments and detection techniques:
Transition to main article topics:
- Advanced detection techniques for colorectal cancer
- New treatment strategies for colorectal cancer
- The impact of advanced detection and treatment strategies on patient outcomes
FAQ
Colorectal Cancer: Advanced Detection And Treatment Strategies For Improved Patient Outcomes is a resource for patients and their families facing the challenges of colorectal cancer. This FAQ section addresses common questions and concerns to provide information and support.
Question 1: What are the most common symptoms of colorectal cancer?
Colorectal cancer often does not cause symptoms in its early stages. As the cancer grows, symptoms may include rectal bleeding, blood in the stool, abdominal pain, unintended weight loss, and changes in bowel habits.
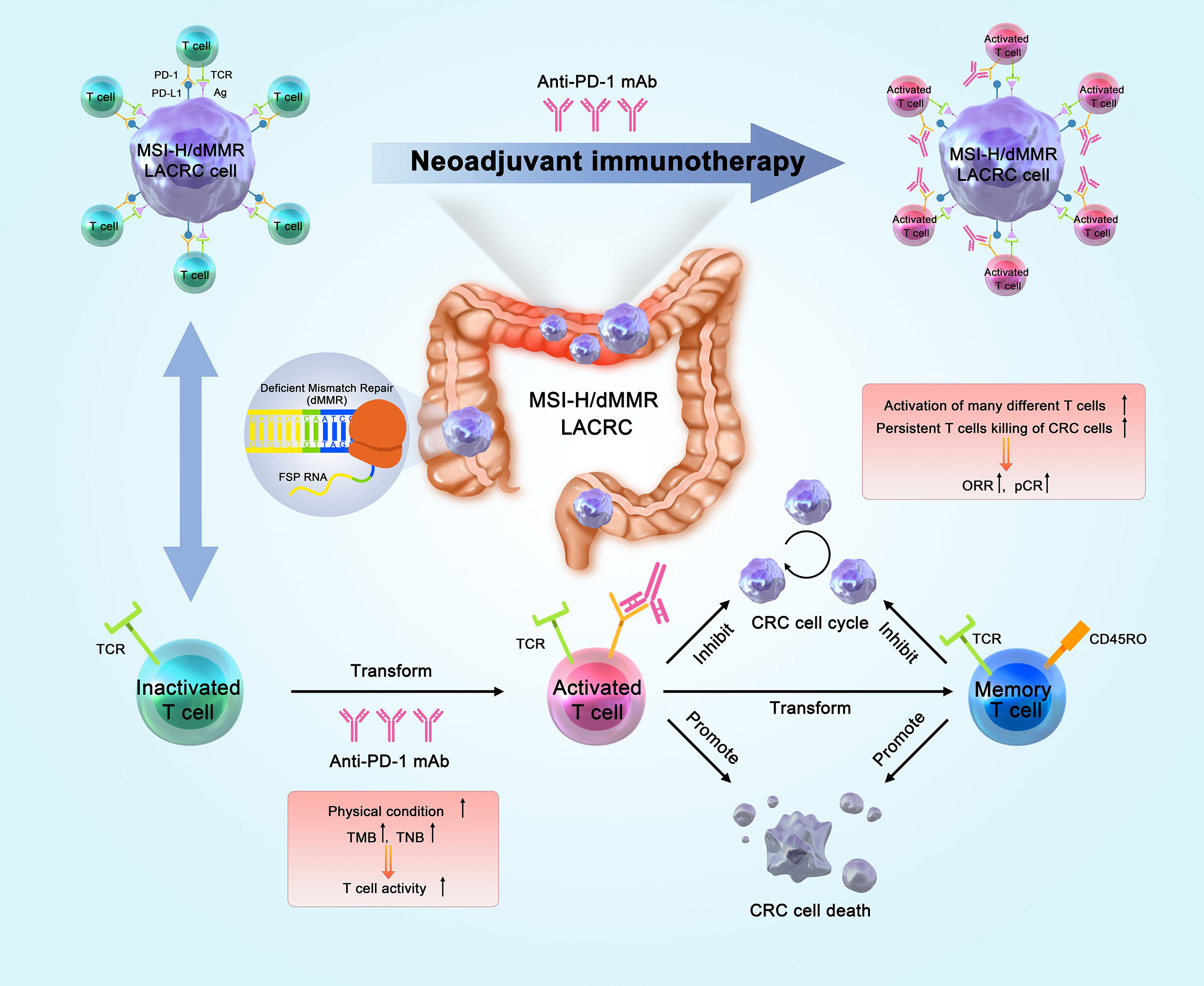
Frontiers | Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy for MSI-H/dMMR Locally Advanced - Source www.frontiersin.org
Question 2: What are the risk factors for colorectal cancer?
Age, family history, personal history of colorectal polyps, inflammatory bowel disease, and certain lifestyle factors such as smoking, obesity, and a diet low in fiber increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
Question 3: What are the different screening tests for colorectal cancer?
Screening tests for colorectal cancer include colonoscopy, flexible sigmoidoscopy, stool-based tests, and virtual colonoscopy. Colonoscopy is the most comprehensive test and allows for the removal of polyps during the procedure.
Question 4: What are the treatment options for colorectal cancer?
Treatment options for colorectal cancer vary depending on the stage of the disease and may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
Question 5: What is the prognosis for colorectal cancer?
The prognosis for colorectal cancer depends on several factors, including the stage of the disease at diagnosis, the patient's overall health, and response to treatment. Early detection and treatment improve the chances of a favorable prognosis.
Question 6: What are the recommended lifestyle changes for reducing the risk of colorectal cancer?
Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, consuming a fiber-rich diet, limiting alcohol intake, and quitting smoking can reduce the risk of colorectal cancer.
This FAQ section provides a general overview of colorectal cancer. For personalized medical advice, consult a healthcare professional.
To learn more about colorectal cancer, its diagnosis, and treatment, visit our website or speak to your doctor.
Tips to Improve Colorectal Cancer Patient Outcomes
An estimated 153,000 individuals are diagnosed with colorectal cancer annually in the United States, making it the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths. Early detection and effective treatment strategies are crucial for improving patient outcomes.
Tip 1: Regular Screening
- Individuals over 45 years of age should undergo regular screening for colorectal cancer.
- Screening options include colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, or stool-based tests.
Tip 2: Know Your Risk Factors
- Certain factors increase the risk of colorectal cancer, including age, family history, obesity, and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Individuals with risk factors should consider more frequent screening or additional testing.
Tip 3: Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and consuming a balanced diet can reduce the risk of colorectal cancer.
- Limit red and processed meats, and increase fiber intake.
Tip 4: Access to Advanced Diagnostics
- Advanced diagnostic techniques, such as CT colonography and MRI, can provide detailed images of the colon and rectum, aiding in early detection and accurate staging.
- These methods can benefit individuals who are unable to undergo traditional colonoscopy.
Tip 5: Multidisciplinary Treatment Approach
- Colorectal cancer treatment often involves a team of specialists, including surgeons, oncologists, and radiation therapists.
- Collaboration among experts ensures a comprehensive approach to disease management.
Tip 6: Access to Clinical Trials
- Clinical trials offer patients the opportunity to access innovative treatments and contribute to medical research.
- Individuals should consider participating in trials when possible to improve their chances of successful treatment.
Tip 7: Patient Education and Support
- Education and support are essential for patients and their families throughout the cancer journey.
- Attend support groups, connect with patient advocates, and utilize reputable online resources.
Tip 8: Long-Term Follow-Up
- Regular follow-up appointments are crucial after treatment to monitor for recurrence and ensure long-term recovery.
- Adhere to follow-up schedules and report any concerning symptoms promptly.
By implementing these tips, healthcare professionals and individuals can collaborate to improve the detection and treatment of colorectal cancer, leading to better patient outcomes.
Colorectal Cancer: Advanced Detection And Treatment Strategies For Improved Patient Outcomes
Colorectal cancer, when detected and treated timely, can yield positive patient outcomes. Advancements in medical technology have introduced innovative strategies that enhance early detection and provide effective treatment plans. This article explores essential aspects of colorectal cancer's advanced detection and treatment methods, highlighting how they contribute to improved patient outcomes.
- Early Detection: Colonoscopies and fecal immunochemical tests (FIT) aid in early detection.
- Genetic Screening: Tests identify individuals at high risk for developing colorectal cancer due to genetic mutations.
- Personalized Treatment: Molecular profiling tailors treatment to a patient's specific genetic makeup.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: Techniques like laparoscopy reduce surgical trauma and promote quicker recovery.
- Immunotherapy: Treatment boosts the immune system's ability to combat cancer cells.
- Multidisciplinary Care: Collaboration among specialists ensures a comprehensive approach to care.
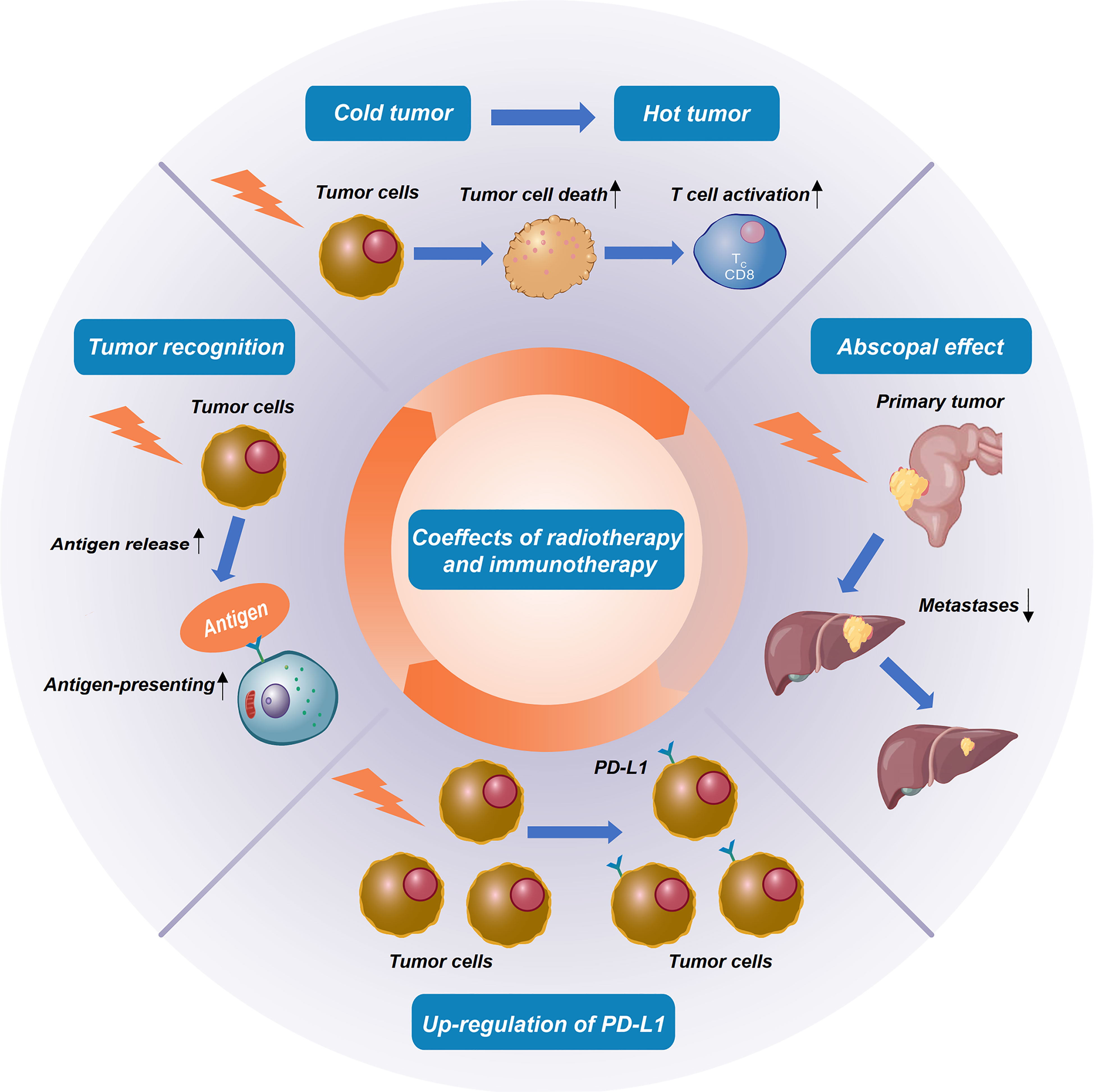
Frontiers | Radioimmunotherapy in colorectal cancer treatment: present - Source www.frontiersin.org
These advanced strategies work in conjunction to improve patient outcomes. Early detection through colonoscopies and FITs enables prompt intervention, while genetic screening identifies high-risk individuals. Personalized treatment and minimally invasive surgery enhance treatment efficacy and reduce side effects. Immunotherapy harnesses the body's own defenses against cancer, and multidisciplinary care ensures seamless coordination among healthcare providers. By embracing these advancements, we can continue to make strides in the fight against colorectal cancer, leading to improved patient outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
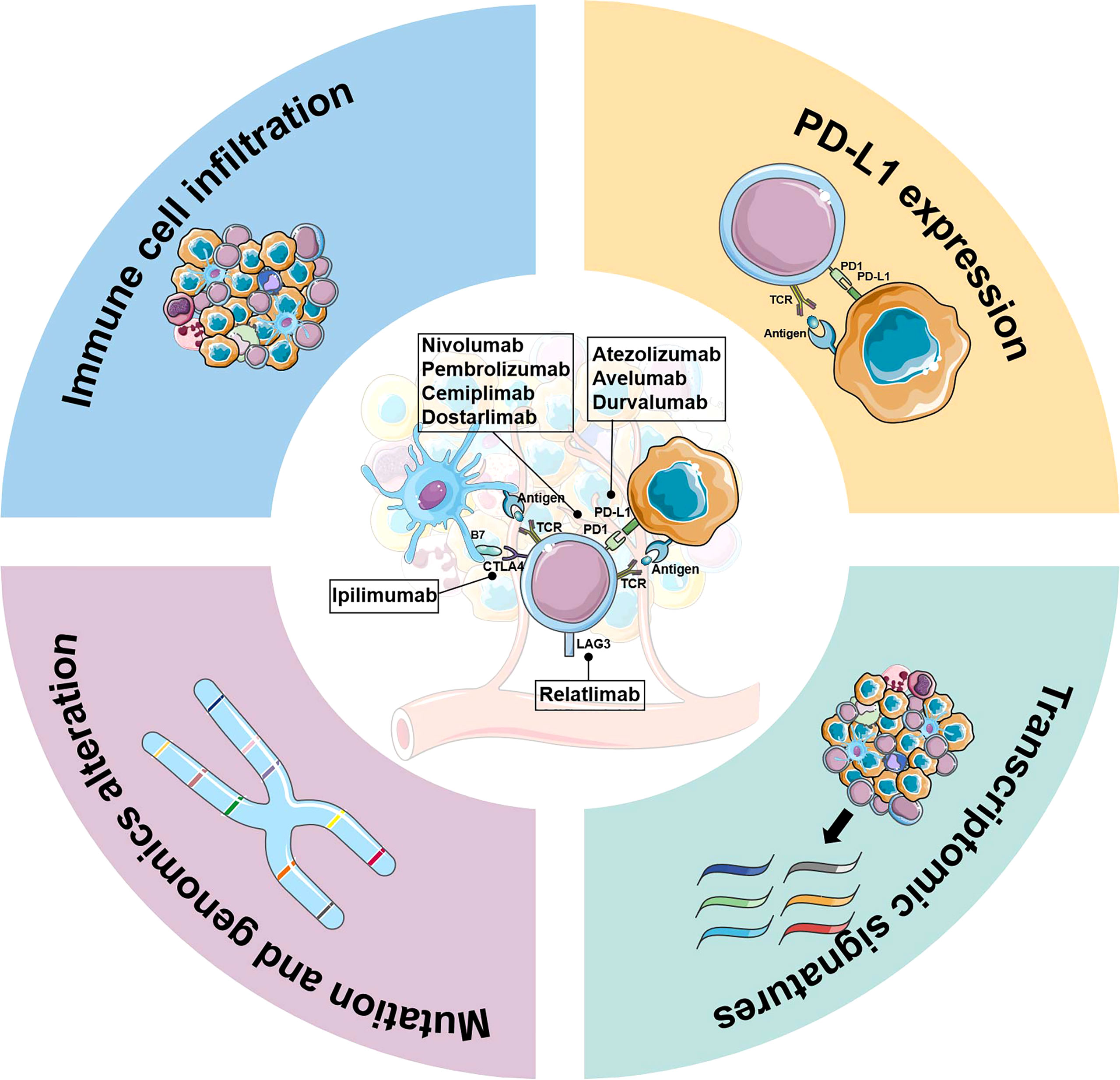
Frontiers | The current landscape of predictive and prognostic - Source www.frontiersin.org
Colorectal Cancer: Advanced Detection And Treatment Strategies For Improved Patient Outcomes
Colorectal cancer is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States, with over 140,000 new cases and 50,000 deaths each year. Advanced detection and treatment strategies are essential for improving patient outcomes and reducing mortality rates.

Multi-omics approaches for biomarker discovery in early ovarian cancer - Source www.thelancet.com
Early detection of colorectal cancer through screening tests such as colonoscopy and fecal occult blood testing is crucial for improving patient outcomes. Screening can detect precancerous polyps and remove them before they develop into invasive cancer. Regular screening is especially important for individuals over the age of 50, who are at higher risk of developing colorectal cancer.
Advanced treatment strategies for colorectal cancer have also improved significantly in recent years. Surgery remains the primary treatment for most patients, but less invasive techniques such as laparoscopic and robotic surgery are now widely used, resulting in better recovery times and reduced complications.
Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies are also increasingly used to treat colorectal cancer, often in combination with surgery. These therapies can help to shrink tumors, reduce symptoms, and improve survival rates. Immunotherapy, which uses the body's own immune system to fight cancer, is a promising new treatment option for some patients with advanced colorectal cancer.
By combining advanced detection and treatment strategies, patient outcomes for colorectal cancer have improved significantly in recent years. Regular screening, less invasive surgical techniques, and targeted therapies have all contributed to reducing mortality rates and improving the quality of life for patients with colorectal cancer.